Industrial PCs are the brains driving many of the machines people and businesses depend on every day, from warehouse robots to national security systems. In the industrial space, applications such as machine vision, industrial robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and deep learning rely on robust, reliable industrial PCs to keep processes running smoothly and effectively.
This article looks at the differences between industrial and commercial PCs, industrial PC advantages, and finding the suitable industrial PC for your application. It also looks at NVIDIA's Jetson platform and the latest graphics processing units (GPUs), vision processing units (VPUs), and tensor processing units (TPUs) for edge AI applications.
How Is an Industrial PC Different from a Commercial PC?
Industrial PCs are designed for specific tasks and applications, ranging from machine vision and vision-guided robotics to AI, security, and surveillance applications. These PCs are similar to commercial PCs in that they receive, store, and process information to perform specific tasks. They also feature similar base components, including the central processing unit (CPU), memory (RAM), motherboard, expansion slots, and often a GPU. Industrial PCs diverge from commercial PCs in several ways, including having a more robust internal and external design, including the computer’s I/O, which is often specialized.
Many industrial PCs offer higher performance specifications, including faster processors, more memory, and additional storage capacity. They are also designed to last longer, have long-term availability, and offer scalability to meet evolving needs due to their ability to be customized or adapted to changing application requirements.
What Are the Advantages of Industrial PCs?
Industrial PCs are designed to have long life cycles, perform complex and specified tasks, and withstand rugged and natural environments that commercial PCs cannot. In addition to having more powerful components, industrial PCs differ from traditional PCs in their physical design. Industrial computer components have larger solders and thicker substrates, with vibration and shock ratings reported as routine specifications. Many industrial computers are also fanless, which limits the amount of dust and particles that can be introduced to internal components, which helps extend device life. Fanless computers leverage internal heat sinks connected to large external heat sink fins to dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
Conformal coatings additionally protect electric components from dust and particles. The external chassis design helps industrial computers respond to temperature changes and movement. It also reduces dust and, in some cases, water infiltration. Multiple mounting options for industrial computers are available, with some designed to accommodate significant vibration and shock.
Some industrial computers resemble traditional desktop or rack systems, but the components, I/O modules, and compute power are nothing like those of an office desktop. Panel PCs, which have an industrial-grade computer integrated directly into the monitor, are also common in manufacturing plants, data control points, and operations locations. Some of these devices are highly ruggedized and can be cleaned with harsh chemicals and firehose-strength liquid jets should the application require them.
Small industrial computers can also be deployed at the edge, bringing them closer to the devices that produce the data. These PCs offer a rugged design, low energy consumption, and a small footprint but still deliver powerful computing performance for various applications, including deep learning and other AI applications.
What Are GPUs, VPUs, and TPUs?
GPU, VPU, and TPU are among the many acronyms commonly seen in industrial computing, particularly regarding AI applications. GPUs, the group's most widely known and deployed, were originally designed to render 3D graphics for video games. In recent years, GPU technology has advanced significantly. Modern GPUs are faster and more powerful than ever before.
A 2023 report on AI from Stanford’s Institute for Human-Centered AI shows that GPUs are approximately 7,000 times more powerful than in 2003 and that price per performance is 5,600 times greater.
GPUs are designed for parallel processing and have become quite popular for their ability to speed up computational processes in compute-intensive applications, including AI and industrial robotics. GPUs are made up of thousands of cores, which are essentially tiny calculators working in parallel to process the math that makes up an AI model, which is—at a high level—how AI computing works, according to NVIDIA.
With each generation of GPUs, the devices are faster and offer more memory. For example, a single NVIDIA GPU can now store an entire AI model.
VPUs, such as the Intel Movidius or the Hailo-15, are system-on-chip (SoC) processors that target AI applications. VPUs are smaller, more power efficient, and less expensive than GPUs, offering system designers and integrators another option for computational power for machine vision and AI at the edge. For example, Intel's Movidius Myriad X VPU interfaces directly with a CMOS image sensor to preprocess images, move them through a pre-trained neural network, and output results while consuming less than 1 W of power.
TPUs, Google's custom-developed application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), are designed to accelerate machine learning applications. Google designed TPUs to handle matrix and vector operations at high speeds, which can accelerate applications on AI frameworks, including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and JAX.
How Do I Choose the Right Industrial PC?
Finding an industrial PC starts with an application analysis. Major considerations include compute power, size, and the application's environment. For example, if AI is involved, the PC may require a GPU or VPU, whereas a telecom application may require data acquisition and communication components such as remote I/O modules.
After analyzing application needs, customers must also consider the following factors:
Space:
How much space do you have for the given application? While space can be a function of system performance, that’s not always the case. Find an industrial PC that strikes a balance between size and performance.
Environment:
Industrial environments can be harsh, subjecting equipment to shock, high vibration, dust, water, or extreme temperatures. Your industrial PC must be rated to handle the environment in which it will be deployed.
Components:
Considerations should include specialty software requirements, processing power, total memory, data storage, I/O options, temperature range, power availability, and physical size needs.
Timing:
How quickly do you need your industrial PC? Certain components may have limited availability, but by working with an expert, you should be able to find alternatives that meet or exceed requirements.
What Is NVIDIA's Jetson? Do I Need It for My Application?
Many high-performance GPUs are large enough to accommodate the heat sinks and fans needed to prevent overheating due to rising power consumption. For its RTX 4090, for example, NVIDIA lists the card at 304 x 137 mm (approximately 12 x 5.4 in.) and three slots wide. Newer formats, like NVIDIA's Jetson platform, can accomplish a range of tasks in a much smaller form factor with significantly less power consumption. A Jetson device is a compact, high-performance system-on-module (SOM) incorporating GPU, CPU, memory, power management, and high-speed interfaces.
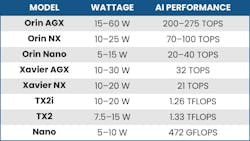
Jetson devices offer high-speed, low-power alternatives to traditional computing platforms. Several models are offered. The table below shows required wattage and AI performance, which is measured in TOPS (tera [one trillion] operations per second), TFLOPS (tera [one trillion] floating point operations per second), or GFLOPS (giga [one billion] floating point operations per second).
Jetson devices offer a powerful means for accomplishing specific tasks such as AI inference but require specific program parameters, whereas larger GPUs have a wide range of applications established for each unit, making them more diverse and general-purpose.
How Have Industrial PC Developments Pushed Automation Capabilities Forward?
The past several years have highlighted the importance of industrial automation. When the pandemic hit, robot order numbers skyrocketed and set new record highs. However, the argument can (and should) be made that automation was ripe for growth regardless. Whether dealing with established automation applications, such as automotive or pharmaceutical manufacturing, or growth areas, such as logistics or food processing, industrial automation systems are more critical than ever to a company's bottom line.
As application needs continually evolve and grow, businesses must find ways to keep pace. This means that industrial automation systems are being tasked with moving faster to increase throughput, quality, and efficiency while maintaining accuracy and effectiveness. This requires much more than just faster cameras. Speeding up automation systems involves additional advancements, such as more flexible robots, novel lighting designs, innovative motion control, advanced AI analysis, and more powerful industrial PCs, which sit at the heart of most automation systems.
About the Author

John DeWaal
President, CoastIPC
John DeWaal is President of CoastIPC, a trusted supplier of industrial and embedded PCs for applications in machine vision, automation, AI, machine learning, and autonomous vehicles. CoastIPC understands the unique requirements of customers in mission-critical applications and can offer custom design, configuration, and deployment services.